Description


Stevia is a common name for the zero-calorie sweetener that is derived from the stevia plant. Stevia leaf is a plant of the Chrysanthemum family, and its leaves have been used as a sweetener in South America for hundreds of years. Extracts from the stevia leaf have been available as dietary supplements in the U.S. since the mid-1990s, and its sweeteners have been permitted for use in foods since 2008. Like all low- and no-calorie sweeteners, stevia may be used to replace sugar and reduce calories in foods and beverages while maintaining sweetness in products that consumers expect.
How is it made?
To make stevia-based sweeteners, the key components are steviol glycosides – the sweet part of leaves. Currently, there are four methods to produce steviol glycosides: extraction, bio-conversion, glucosylation and fermentation.
Extraction
This was the original production method for stevia-based sweeteners. During this process, stevia leaves are crushed and steeped in hot water. The mixture is filtered to separate the liquid plant extract from the leaves. The extract is purified again and produces a sweetener that contains various steviol glycosides.
Bioconversion
This process begins with steviol glycosides that have already been extracted from the stevia leaf. Bioconversion replicates the stevia plant’s natural maturation process, using enzymes to convert various, different steviol glycosides into specific, targeted steviol glycosides such as Rebaudioside M (abbreviated Reb M) and Reb D. Although the enzymes used in this production method are derived from genetically modified micro-organisms, the subsequent purification process(es) remove all enzymes and/or micro-organisms from the final product.
Glucosylation
As a foundation, glucosylation also uses steviol glycosides that have been extracted from stevia leaves. In this production method, enzymes are used to add glucose units, which produces a combination of steviol glycosides. All enzymes and/or micro-organisms are removed from the final product to deliver purified stevia extract.
Fermentation
Fermantation also replicates the plant’s natural genetic process to create steviol glycosides. In the fermentation production method, steviol glycosides are produced by genetically modified micro-organisms that convert sugars into steviol glycosides like Reb M and Reb D. As with the other processes that may involve enzymes and micro-organisms, the extract is refined to remove those components and produce high-quality stevia extract.
How sweet is it?
The sweetness is approximately 200-300 times sweeter than sugar, so only a tiny amount is needed to give a sweet taste.
What foods contain stevia?
It may be found in a variety of foods and beverages around the world, including reduced-calorie beverages, bread, tea, and yogurt. It is also available as a tabletop sweetener.
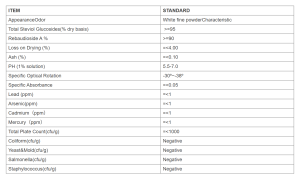
Specification
FAQ
1, Is Health Sweet a manufacturer or just a trading company?
We are both manufacturer and trading company, we are distributor, at the same time, we are manufacturer of D-mannose.
2, What is the Min Order Quantity of Stevia ?
Different products have different MOQ, this product MOQ is 1000kgs.
3, What is the price ?
We are a famous supplier and manufacturer in China, and has been corporate with many suppliers for several years, we can provide you with cost-effective product.
4, How long shall we wait for your reply?
We can guarantee to reply your inquiries in less than 2 hours in working days.
5, What kinds of transportation types can you provide?
Our main transportation methods include air transportation, land transportation and water transportation.
6, What kinds of payment terms can you accept?
The most commonly used payment terms are T/T, L/C, D/P, D/A, etc.
7, How long will I receive my good?
We have own warehouse in Qingdao and Dalian, when your purchase order has been confirmed, inventory products will deliver within 1 week, other products delivery in 2 weeks.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.