What’s Aspartame powder ?

Aspartame is a low-calorie artificial sweetener, which is approximately 200 times sweeter than sugar. It is a white, odorless powder.
In Europe, aspartame powder is authorised to be used as a food additive to sweeten a variety of foods and beverages such as drinks, desserts, sweets, dairy products, chewing gum, low-calorie and weight control products, and as a table-top sweetener.
In the EU, as for all food additives, the presence of aspartame powder must be indicated on the label either by its name or its E number (E 951).
The sweetener and its breakdown products have been authorised for human consumption for many years following thorough safety assessments.
In the European Union, all food additives that were already permitted for use prior to 20 January 2009 need to undergo a safety re-evaluation by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA).
Aspartame (E 951) powder was one of the first food additives to be fully re-evaluated by EFSA in 2013.
Why Do People Use Aspartame powder ?
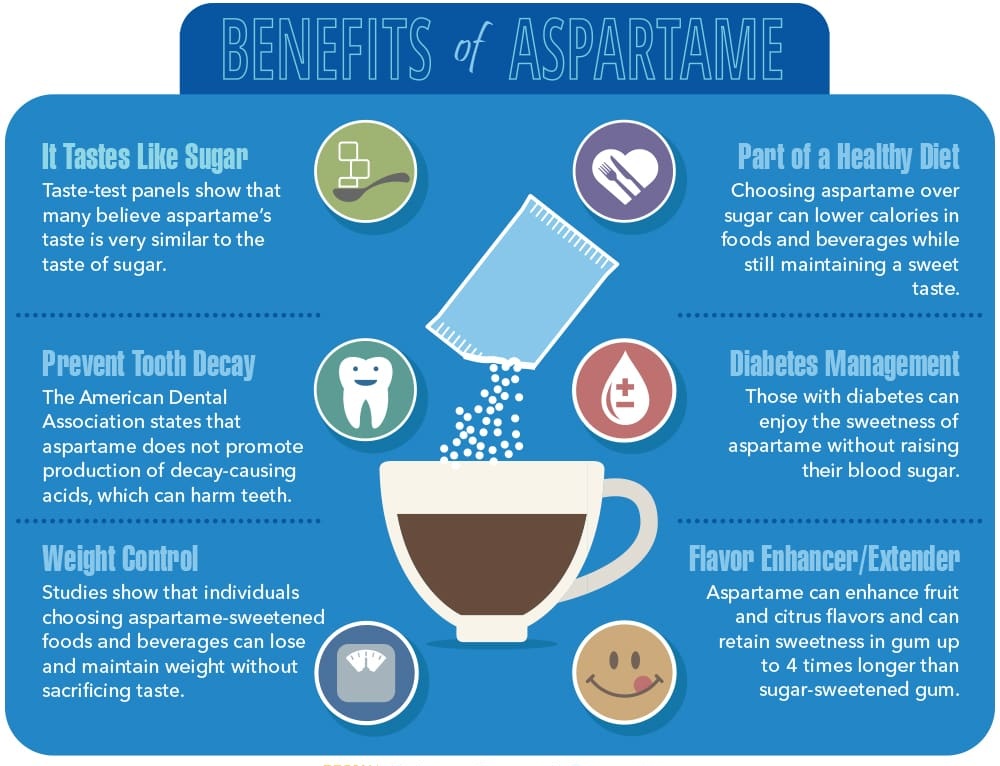
Aspartame powder is one of the most common artificial sweeteners in the United States. It first entered the food market in 1981 and continues to be a replacement for sugar in soda, candy, and diet foods. It’s the main ingredient in popular zero-calorie sugar substitutes like Nutrasweet® and Equal® and can be found in Diet Coke, Trident chewing gum, and sugar-free products, such as sugar-free pancake syrup.
People use artificial sweeteners like aspartame powder to cut back on the number of calories they consume and to help manage their blood sugar levels. For example, a twelve-ounce serving of regular Coke contains 140 calories and 39 grams, or 9.75 teaspoons, of added sugar, while the same serving of Diet Coke provides zero calories and zero grams of sugar.
Unlike caloric sweeteners, like table sugar and corn syrup, aspartame has a minimal effect on blood sugar levels, which is why it’s often recommended to people with prediabetes and diabetes.
Additionally, because artificial sweeteners contain virtually zero calories, many people view artificially-sweetened foods and drinks as “healthier” than products that are sweetened with sugar.
However, the regular consumption of artificial sweeteners has been linked to several health issues, which is why the safety of many artificial sweeteners, including aspartame, has been questioned by scientists and healthcare providers for decades.
Usage of Aspartame powder
- Soft Drinks.
- Fruit Juice
- Yogurt
- Jams & Jellies
- Chewing Gums
- Candies

Is Aspartame Bad For You?
High consumption of aspartame-containing products, such as diet soda, has been linked to several health concerns. However, the research is still ongoing.
Recently, The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)—the cancer agency of the World Health Organization (WHO)—classified aspartame as a Group 2B carcinogen. Group 2B carcinogens are considered possibly carcinogenic to humans, meaning they may have the potential to cause cancer.
The agency classified aspartame powder as Group 2B based on limited evidence that consuming aspartame may cause cancer in humans. This does not mean consuming aspartame will necessarily result in cancer. However, it suggests diets very high in aspartame may be harmful to health and may increase the risk of some cancers with excessive consumption.
A study that included data on 102,865 people found high consumers of total artificial sweeteners, including aspartame, had a 13% higher risk of overall cancer compared to non-consumers. The study found the use of aspartame and another artificial sweetener called acesulfame-K had the strongest association with increased cancer risk.
It should be noted the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued a statement that it disagrees with IARC’s classification of aspartame powder as a possible carcinogen to humans.
Possible Side Effects of Aspartame powder

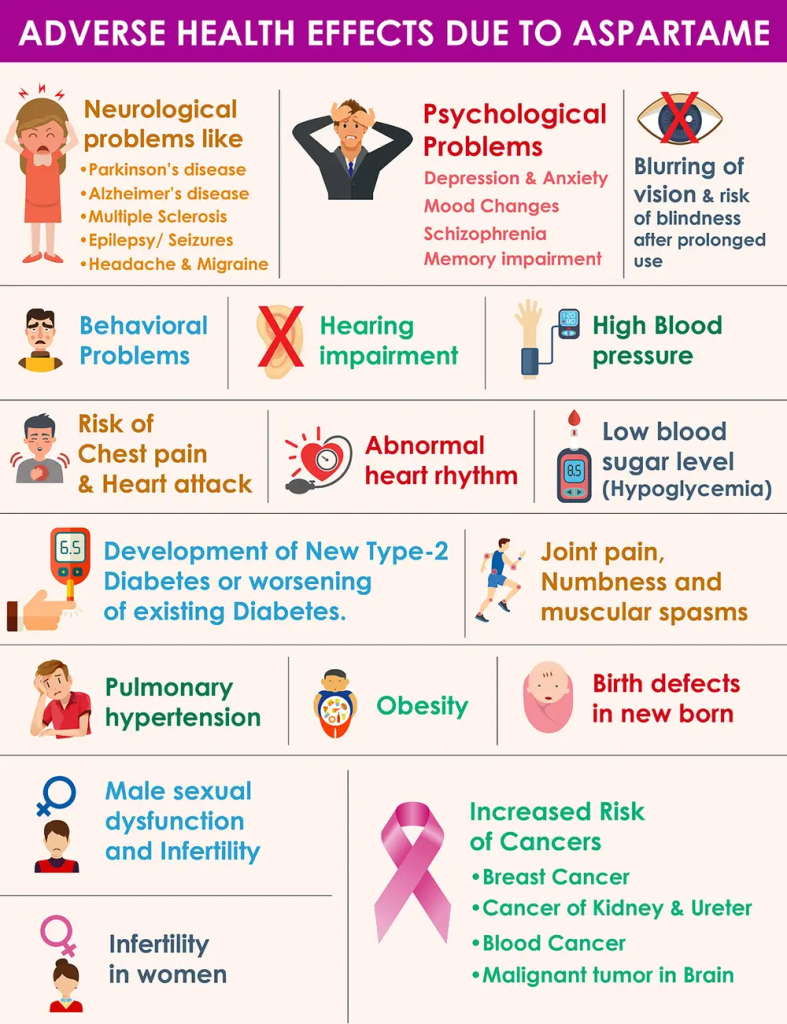
In addition to potentially causing an increased cancer risk, diets high in aspartame have been linked to other health concerns. However, many of the findings on aspartame and health are inconsistent, meaning some studies have shown aspartame can negatively impact health while others have found no effect.
1.May Harm the Microbiome
2.May Negatively Impact Blood Sugar Control
3.May Negatively Impact Brain Health
4.May Harm Heart Health
How Much Aspartame Is Too Much?
Although organizations like the IARC have linked aspartame to some health concerns, the FDA considers aspartame to be safe for human consumption. According to the FDA, aspartame is safe in doses under 50 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day.
To reach the upper end of the Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI), a person weighing 132 pounds would need to consume around 75 packets of aspartame sweetener in a single day.
This level of aspartame consumption would be difficult to reach on a daily basis, which is why organizations like the FDA still consider aspartame, and other artificial sweeteners linked to increased cancer risk, as safe for human consumption.
However, recent research has made it unclear if levels lower than the ADI harm health. Some evidence suggests people who regularly consume artificially-sweetened beverages and consume artificial sweeteners well under the current ADI are at a greater risk of some health issues, including dementia and stroke.
Who Should Avoid or Limit Aspartame?
Certain groups of people may need to avoid aspartame powder and aspartame-containing products for health reasons.
For example, people who have phenylketonuria (PKU) need to avoid aspartame. PKU is a genetic disorder in which the body lacks the enzyme needed to break down an amino acid called phenylalanine. Aspartame contains phenylalanine, so it’s not appropriate for people with PKU. A lifelong low-phenylalanine diet is the primary treatment option for people with this condition.
Additionally, some evidence suggests aspartame may increase the risk of cancer, specifically liver cancer. While more research is needed, people who are at a higher risk of liver cancer, such as people with chronic viral hepatitis, people with obesity, and people with type 2 diabetes, may want to limit their intake of aspartame and aspartame-containing foods.
A Quick Review
Aspartame is an artificial sweetener found in a variety of foods and drinks, such as diet soda and sugar-free sweets.
Aspartame has zero calories and is often recommended as a blood sugar-friendly sweetener. However, diets high in aspartame have been linked to a few health concerns, including an increased risk of heart disease and cancer.
While artificial sweeteners like aspartame are considered safe by regulatory agencies like the FDA, research on their long-term safety is ongoing.


