Description

Soy Lecithin is a food additive that comes from several sources — one of them being soy. It’s generally used as an emulsifier, or lubricant, when added to food, but also has uses as an antioxidant and flavor protector.
Like many food additives, soy lecithin isn’t without controversy. Many people believe it carries potential health dangers. However, few, if any, of these claims are backed by concrete evidence.
You may already be taking it
Soy lecithin is found in dietary supplements, ice cream and dairy products, infant formulas, breads, margarine, and other convenience foods. In other words, you’re probably already consuming soy lecithin, whether you realize it or not.
The good news is that it’s usually included in such small amounts, it isn’t something to be too concerned about.
Some people take lecithin supplements in addition to consuming it in their diet. Research has shown that supplemental lecithin may offer health benefits, from lowering cholesterol to improving ulcerative colitis symptoms.
Lecithin is the collective name for a group of lipids, or fatty compounds, naturally found in foods like eggs, fish, milk, and soybeans. The food industry also uses lecithin as an emulsifier, which helps keep substances from separating.
Lecithin supplements are made of different amounts of phospholipids. These fats are found in all animal and human cells and are involved in cellular communication and inflammation regulation. Read on to learn about lecithin supplements, including possible benefits and risks.

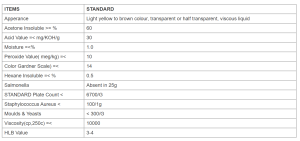
Specification
Health Benefits of Soy Lecithin
1.Can Help Manage Ulcerative Colitis
The phospholipid phosphatidylcholine is concentrated in lecithin and forms part of the intestinal mucus barrier, which protects the intestinal lining.
This phosphatidylcholine content of the intestinal mucus barrier is reduced in people with ulcerative colitis. This digestive disorder is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Some evidence suggests that lecithin supplements may replenish the intestinal mucus barrier in people with ulcerative colitis. Lecithin may also improve inflammatory activity.
A review published in 2021 found that delayed-release lecithin supplements that contain 30% phosphatidylcholine could improve disease activity in people with ulcerative colitis. The researchers also found that these participants had an increased quality of life.
2.Helps Infants and Parents Who Are Nursing
Lecithin is rich in phosphatidylcholine, which is a source of choline. This nutrient is needed for cellular health, immune function, metabolism, and more. Choline is especially important during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as it supports fetal and infant brain development.
Infants born prematurely might have supplemental lecithin added to breast milk that’s pumped to them through a plastic tube. The addition of lecithin can prevent fat loss.
3.May Improve Cholesterol Levels
Research has shown that lecithin supplements can benefit cholesterol levels. More and larger studies are needed to say how lecithin supplements impact cholesterol levels.
Some evidence suggests that lecithin lowers LDL (“bad”) cholesterol by stimulating the secretion of bile acid. Bile acid is produced from the breakdown of cholesterol.
4.Might Reduce Heart Disease Risk
Diastolic blood pressure is the bottom number on a reading. It measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats. High blood pressure increases your risk of several conditions, including heart disease.
A study published in 2018 of 89 middle-aged Japanese women found that supplementation with 1,200 milligrams (mg) of soy lecithin for eight weeks reduced diastolic blood pressure levels compared to a placebo. The participants also had a reduced cardio-ankle vascular index. This marker assesses the stiffness of arteries, which is a risk factor for heart disease.
Good Sources of Soy Lecithin
Egg yolks are one of the richest sources of dietary lecithin, providing around 250 mg of lecithin per large yolk. The word “lecithin” comes from “lekithos,” which is the Greek word for egg yolk.
Other sources of dietary lecithin include:1213
- Canola oil
- Corn oil
- Fish
- Organ meat
- Peanuts
- Soybeans and soybean oil
- Sunflower seeds
- Wheat germ
Is Soy Lecithin Safe?
Lecithin is generally recognized as a safe ingredient in food. It also seems to be safe in supplement form.
It’s unknown whether high-dose supplementation is safe for infants or people who are breastfeeding.
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2024. Lecithin supplements may also pose a safety risk to those allergic to eggs and soy. Many of the supplements are derived from these allergens. Those who have such allergies and take lecithin might experience a reaction like a skin rash.
What To Look For Soy Lecithin
It’s important to purchase products from reputable companies. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) doesn’t regulate dietary supplements in the same way as medicine. Manufacturers aren’t required to prove supplements’ safety or effectiveness before the products are sold to consumers.
It’s best to research companies before you start shopping for lecithin supplements. Choose lecithin supplements from companies that use third-party labs to test their products for quality and purity, such as those certified by organizations like NSF International.
Consider purchasing a powdered lecithin supplement if you can’t tolerate swallowing capsules. Be sure to check the label to find out how many capsules or how many scoops of powder are required to meet the dosage recommendation.
Can You Take Too Much?
Lecithin is considered safe, but there’s a lack of research on adverse side effects at high doses. It’s important not to take more than what is indicated on the packing. Speak to a healthcare provider if you have questions about dosing.
Side Effects of Lecithin
Lecithin is usually well-tolerated, but it may cause side effects like:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Nausea or vomiting
Lecithin is naturally found in foods like egg yolks, liver, and soybeans. It can also be taken as a dietary supplement. Lecithin supplements may reduce cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and improve ulcerative colitis symptoms. They also provide a source of choline, which is essential for cellular health and nervous system function.
Most healthy people get plenty of lecithin through their diet and don’t need to take supplemental lecithin. Be sure to speak to a healthcare provider if you’re interested in taking a lecithin supplement.
FAQ
1, Is Health Sweet a manufacturer or just a trading company?
We are both manufacturer and trading company, we are Soy Lecithin distributor, at the same time, we are manufacturer of other products.
2, What is the Min Order Quantity of Soy Lecithin?
Different products have different MOQ, for Soy Lecithin, the MOQ is 1000kgs.
3, What is the price of Soy Lecithin?
We are a famous supplier and manufacturer of Soy Lecithin in China, and has been corporate with many Soy Lecithin suppliers for several years, we can provide you with cost-effective Soy Lecithin.
4, How long shall we wait for your reply?
We can guarantee to reply your inquiries of Soy Lecithin in less than 12 hours in working days.
5, What kinds of transportation types can you provide?
Our main transportation methods include air transportation, land transportation and water transportation.
6, What kinds of payment terms can you accept?
The most commonly used payment terms are T/T, L/C, D/P, D/A, etc.
7, How long will I receive my good?
We have own warehouse in Qingdao and Dalian, when your purchase order has been confirmed, inventory products will deliver within 1 week, other products delivery in 2 weeks.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.